What Is Needed to Use a 12 Volt Hoist With Ac Current
Fusing Guide Overview Fuses are disquisitional in any electrical system and are used to protect a circuit'southward cabling from excessive current that could pb to harm and, very often, an electrical fire. Excessive current is most likely to be caused past three things:
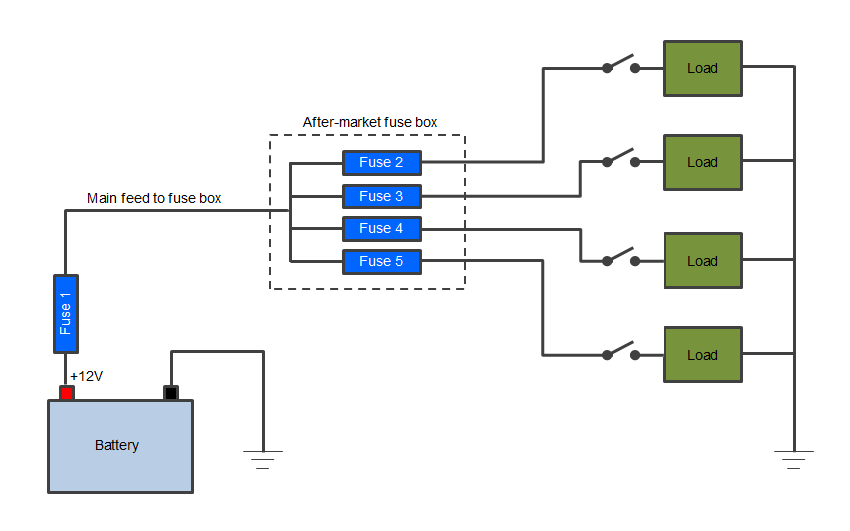
Where and when to utilise fuses In an ideal world each private department of positive cable would exist fused as this would provide the nigh protection and make mistake finding relatively straight forward, because it would allow y'all to narrow downwards the problem to a single section of cable (i.e. where the fuse has blown). Having said that this is platonic it is virtually always impractical as it would lead to many fuses fitted throughout an electric system. A good compromise is that every individual excursion should exist fused equally this provides a good caste of protection and at least allows you to narrow downwardly the problem to 1 circuit. It is important to annotation that the department of cable coming from the battery +ve terminal to the first fuse (or bombardment distribution box) is effectively an unprotected part of the circuit. If there is a short anywhere forth this length then information technology is very likely to catch burn down as the first fuse volition non experience the excess electric current. For this reason the length of cable from the battery +ve to the first fuse should be equally brusque equally possible and then that damage is minimised in the event of an electrical fire. Fusing Exceptions There are some instances where fuses are not ordinarily used and 1 instance is for the, normally short, length of cable from the battery to the starter motor. Starter motors are usually the highest current draw electric item on a vehicle every bit they have to crank the engine, and the current can reach several hundred Amps, especially with large diesel fuel engines that take a high compression ratio. For this reason it is usually deemed impractical to fuse this length of cablevision, although some vehicles practise take fusible links which are simply a minor department of lower electric current rating cable encased in a fireproof sleeve. They are installed with the cable being protected and are designed to melt and break the circuit in an over-electric current status. The other reason for not fusing the starter circuit is that if the bombardment is disconnected from the alternator whilst information technology is turning (as would be the example if a fuse blew) the diodes in the alternator's rectifier can be damaged. To offer an increased level of safety it is mutual in many race automobile, kit machine, custom machine and leisure vehicle builds to fit a bombardment cut-off or main switch that can be manually operated to isolate the primary battery or auxiliary batteries from the rest of the vehicle'southward electric arrangement in the effect of a problem. Typical after-market fusing arrangement The following diagram shows how electrical loads such every bit lights etc. might be fused in an after-market circuit. Annotation that the primary feed from the bombardment is fused to protect this section of cable and this cable should be large enough to supply the current required past all the loads operating at the same fourth dimension (worst case). Consequently the fuse used for this cable (fuse 1) volition be of a college rating than fuses 2-5 (run into below for selecting a fuse rating). Each of the 4 circuits supplying the loads are then fused individually in the fuse box at the beginning of each circuit (and before the switches). This is important because if a section of cable shorts to footing it will simply be protected if there is a fuse before the shorting point (otherwise the fuse will not experience the excess current because it will be outside of the short-circuit). Fuse ratings
In simplified terms the greater the current is above the continuous rating, the faster the fuse will blow. For instance, if a 10A fuse is exposed to 11A then it might take many minutes for it to blow but if information technology is exposed to 20A then it may blow in a fraction of a second. Manufacturers show this blow time on a Current-Time chart merely for the typical user it's non necessary to go into this level of technical particular every bit long as you follow some bones fuse selection guidelines every bit described in the next section: Selecting the correct fuse rating If replacing a blown fuse in a manufacturer-designed (factory) application, eastward.g. in a vehicle fuse panel, then the same type and rating of fuse should be used. If a fuse continues to blow and then there must be a fault with the circuit and a higher rating fuse should never exist fitted to overcome this, even temporarily. Doing this creates a high risk of component failure and electrical fire. When specifying a fuse for an later-market application, the key consideration is that the fuse should exist the weakest point (i.eastward. lowest rated component) so that it e'er blows before any harm occurs to other parts of the electrical circuit. However, yous as well practice not want the fuse to keep blowing nether normal operation (known every bit a nuisance accident), and then the two elements to consider are:
>The fuse rating should lie somewhere betwixt these ii values to let normal operation but blow on overload. For example, if the normal expected current depict is 10A and the cablevision size is 25A, then a fuse rated at 15A would be appropriate. Types of Fuse In that location are several types of fuse currently in use in the automotive market place and the table below gives a cursory description of each:
Circuit Breakers What is a circuit breaker? Excursion breakersprovide overload protection for the circuit in the same way that a fuse does (past breaking the circuit continuity) but, dissimilar a fuse, can be reset rather than having to be replaced. These are useful in applications where, due to their nature, an over-current condition is expected to occur now and again under normal use and to take to frequently supercede fuses would be inconvenient (e.g. electrical motors used for winches, power windows etc.). They are also useful where you might need to reset the excursion rapidly and don't want to spend time looking for a fuse. How do they piece of work? Most excursion breakers establish in 12V or 24V systems operate thermally. The heat generated by the excess current during an overload causes the contacts inside the billow to come up apart and break the excursion. These are so reset either manually or automatically depending on the design of the circuit breaker. Circuit breakers that have to be manually reset provide an opportunity to cheque for whatever problems before using the circuit again and on some types you can manually trip the breaker, which is useful for isolating the circuit and for testing the billow. Fuses vs excursion breakers Whilst circuit breakers are very useful solution in certain applications it should be noted that a good quality fuse volition ultimately be more reliable (there are no moving parts) and so should be considered outset, and where sensitive electronic equipment is involved a circuit breaker should never exist used. This is considering the time taken for the circuit breaker to operate tin can be longer than it would have a traditional fuse to blow, potentially exposing the circuit to dissentious overload currents for longer. Disclaimer The information independent in these articles is provided in practiced organized religion and nosotros practise our best to ensure that it is accurate and up to engagement, even so, we cannot exist held responsible for any impairment or loss arising from the employ or mis-utilize of this information or from any errors or omissions. The installer is ultimately responsible for the prophylactic of the organisation and then if you are in whatever doubt, please consult a qualified electrician. | Watch our YouTube "how to" guides here Find out about our Trade Accounts here |
Source: https://www.12voltplanet.co.uk/fuses-guide-uses.html












Post a Comment for "What Is Needed to Use a 12 Volt Hoist With Ac Current"